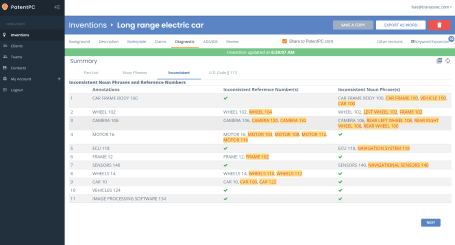
Introduction
In a world driven by innovation and technological advancement, patents play a pivotal role in protecting the intellectual property rights of inventors and fostering economic growth. However, the global nature of innovation has led to an increasingly interconnected web of patent systems, each with its own set of rules and regulations. Patent harmonization, the process of aligning and standardizing patent laws and procedures across different jurisdictions, has emerged as a critical endeavor to streamline the global patent landscape. This article explores the ongoing efforts, achievements, and challenges in the realm of patent harmonization.

The Need for Patent Harmonization
As innovation knows no borders, the need for a unified and coherent patent system becomes evident. The lack of harmonization often results in inefficiencies, increased costs, and legal complexities for inventors and businesses operating on a global scale. Harmonizing patent systems seeks to create a level playing field, reducing barriers to entry for inventors and encouraging the free flow of ideas and technologies across borders.
1. The Globalization of Innovation
Innovation knows no boundaries. Companies and inventors are no longer confined by geographical constraints, often operating on a global scale to leverage diverse expertise and resources. As a result, the current patchwork of national patent systems poses significant challenges for those seeking protection for their inventions across multiple jurisdictions. Patent harmonization is crucial to facilitate the seamless protection of intellectual property rights in a world where innovation is inherently global.
2. Streamlining Patent Filing Procedures
One of the primary objectives of patent harmonization is to streamline the often complex and divergent procedures associated with filing patent applications. Currently, inventors face a labyrinth of rules and requirements when seeking protection in different countries. Harmonization, as exemplified by initiatives like the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), offers a pathway for inventors to file a single international application that is recognized by multiple countries, significantly reducing the administrative burden and costs associated with filing separate applications in each jurisdiction.
3. Enhancing Legal Certainty and Predictability
The lack of uniformity in patent laws among countries introduces legal uncertainty for inventors and businesses. Harmonizing patent laws would create a more predictable environment, where the criteria for patentability and the scope of protection are standardized. This, in turn, allows inventors to make informed decisions about pursuing patent protection for their innovations without the ambiguity arising from differing legal standards.
4. Reducing Costs and Administrative Burden
Navigating the intricacies of multiple patent systems can be financially burdensome, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and individual inventors. Harmonization efforts aim to alleviate these financial barriers by creating a more cost-effective and efficient system. By reducing the need for multiple filings, translations, and legal consultations, patent harmonization can democratize access to patent protection and spur innovation across a broader spectrum of entities.
5. Fostering International Collaboration
Patent harmonization transcends the legal realm; it is also a catalyst for international collaboration. A harmonized patent system encourages cooperation among inventors, research institutions, and industries worldwide. It promotes the sharing of knowledge and technologies, facilitating a collaborative environment where breakthroughs in innovation can be accelerated through a collective effort. Such collaboration is especially crucial in addressing global challenges, such as climate change, public health crises, and other issues that require coordinated solutions.
6. Addressing the Rise of Emerging Technologies
The advent of emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and biotechnology, presents novel challenges for patent systems worldwide. Harmonization becomes imperative to ensure that these technologies receive consistent and fair treatment across jurisdictions. Without a unified approach, disparities in the protection of inventions in emerging fields may hinder the growth and deployment of transformative technologies on a global scale.
7. Strengthening the Rule of Law
A harmonized patent system contributes to the broader goal of strengthening the rule of law at the international level. By fostering a shared commitment to the protection of intellectual property rights, harmonization builds a foundation for a rules-based global order. This not only benefits inventors and businesses but also promotes a fair and equitable framework for addressing disputes and ensuring the just enforcement of patent rights across borders.
8. Encouraging Innovation in Developing Economies
Developing economies often face challenges in establishing robust patent systems that can attract investment and stimulate local innovation. Harmonization provides an opportunity for these economies to align their patent laws with international standards, making them more attractive to foreign investors and fostering a conducive environment for innovation. This, in turn, can contribute to economic development and technological progress on a global scale.
International Treaties and Agreements
One of the primary mechanisms for patent harmonization is the establishment of international treaties and agreements. The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS), administered by the World Trade Organization (WTO), stands out as a milestone in this regard. TRIPS sets minimum standards for intellectual property protection, including patents, and provides a framework for member countries to harmonize their national patent laws.
Additionally, the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) offers a mechanism for filing a single international patent application that is recognized by multiple countries, streamlining the process for inventors seeking protection in multiple jurisdictions. The PCT has significantly contributed to harmonizing filing procedures and reducing the administrative burden associated with seeking patent protection globally.
Regional Harmonization Efforts
In addition to global initiatives, various regions have undertaken harmonization efforts to facilitate innovation and economic development within their boundaries. The European Patent Office (EPO) and the European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) have worked towards creating a unified patent system within the European Union. The Unitary Patent and the Unified Patent Court, once fully implemented, aim to simplify the process of obtaining and enforcing patents across participating EU member states.
Similarly, in Southeast Asia, the ASEAN Patent Examination Cooperation (ASPEC) program seeks to harmonize patent examination practices among member states. By promoting the exchange of information and best practices, ASPEC aims to enhance the quality and efficiency of patent examination, ultimately fostering innovation in the region.
Challenges in Patent Harmonization
Despite the noble goals of patent harmonization, the path to a fully streamlined global patent system is fraught with challenges. These challenges range from legal and cultural differences to the sheer complexity of aligning diverse patent systems.
1. Legal and Cultural Diversity
One of the fundamental challenges in patent harmonization is the vast legal and cultural diversity among countries. Legal traditions, language barriers, and cultural differences can impede the development of a universally accepted set of patent laws. Bridging these gaps requires a delicate balance between respecting each country’s sovereignty and establishing common ground for the protection of intellectual property rights.
2. Differing Patentability Criteria
Countries often have different criteria for patentability, making it challenging to create a standardized set of rules. For example, some jurisdictions may have stricter or more lenient standards for novelty, non-obviousness, and industrial applicability. Harmonizing these criteria without compromising the essence of patent protection poses a significant challenge.
3. Implementation and Enforcement
Even when harmonization efforts result in agreed-upon standards, the implementation and enforcement of these standards can vary widely. In some cases, countries may adopt harmonized laws but struggle with effective enforcement due to resource constraints, legal infrastructure, or other practical challenges.
4. Opposition from Stakeholders
Stakeholders, including industries, patent offices, and legal professionals, may resist harmonization efforts if they perceive potential drawbacks to their interests. For example, industries accustomed to favorable conditions in a particular jurisdiction may resist changes that could impact their competitive advantage. Addressing these concerns and garnering support from diverse stakeholders is crucial for successful harmonization.
Recent Successes in Patent Harmonization
While challenges persist, recent years have witnessed notable successes in patent harmonization efforts. These successes demonstrate the potential for overcoming obstacles and creating a more cohesive global patent system.
1. The Hague Agreement Concerning the International Registration of Industrial Designs
The Hague Agreement, administered by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), provides a simplified and cost-effective mechanism for the international registration of industrial designs. By allowing applicants to register their designs in multiple countries through a single application, the Hague Agreement contributes to harmonizing the protection of industrial designs on a global scale.
2. The Patent Law Treaty (PLT)
The PLT, administered by WIPO, aims to streamline and harmonize formal procedures associated with patent applications. By establishing common standards for practices such as filing dates, representation, and the format of patent applications, the PLT reduces administrative burdens for both applicants and patent offices. As of [current year], [number] countries have acceded to the PLT, marking a significant step towards global harmonization of patent procedures.
3. The America Invents Act (AIA)
At the national level, the United States has taken steps towards harmonizing its patent system with international standards through the America Invents Act. The shift from a “first-to-invent” to a “first-inventor-to-file” system aligns the U.S. patent system more closely with the practices of many other countries, contributing to greater consistency in global patent procedures.
Future Prospects and Emerging Trends
As the world continues to advance technologically, the importance of patent harmonization will only grow. Several trends and developments offer insights into the future prospects of patent harmonization efforts.
1. Digital Transformation and Artificial Intelligence
The digital transformation of industries and the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) present new challenges and opportunities for patent harmonization. As AI technologies become more prevalent, questions surrounding inventorship, ownership, and patentability criteria for AI-generated inventions will require careful consideration and international cooperation.
2. Green Technology and Sustainable Innovation
The global focus on sustainability and green technologies introduces another layer of complexity to patent harmonization. Harmonizing the protection of inventions in areas such as renewable energy, waste management, and eco-friendly technologies is crucial for addressing environmental challenges on a global scale.
3. Collaboration and Information Sharing
Advancements in technology have facilitated greater collaboration and information sharing among patent offices worldwide. Platforms for sharing prior art, examination results, and best practices contribute to more consistent and efficient patent examination processes, fostering a culture of collaboration among patent offices.
Conclusion
The journey towards patent harmonization is undoubtedly challenging, but the efforts made thus far have laid a foundation for a more cohesive global patent system. As technology continues to evolve, the need for a harmonized approach to intellectual property protection becomes increasingly urgent. While challenges persist, recent successes, emerging trends, and a shared recognition of the benefits of harmonization provide hope for a future where inventors can navigate the global patent landscape with greater ease and efficiency. By addressing the remaining challenges and embracing ongoing collaborative efforts, the international community can contribute to a world where innovation knows no borders, and intellectual property rights are safeguarded on a truly global scale.